The 4 Disruptive Technologies Reshaping Insurance Operations
Technology usage in the insurance industry has come a long way since the initial days of first-generation computers. Back then, computers made data collection and tabulation simpler – a great disruptive technology of the mid-1950s indeed!
The technological landscape since then has evolved leaps and bounds, with digitalization in insurance permeating almost every process. From policy pricing, claims management and customer service to underwriting and even risk analysis, technology has disrupted many key functions. Stats show that the power of digitization of insurance for a typical large auto insurer in The United States is a doubling of profitability over 5 years (McKinsey report). If that does not clinch the debate about the effect of new technology in disruptive insurance as we know it, nothing else will. Here is more on the technologies that are bringing in a revolution.
Disruptive Technology DefinitionDisruptive technology is any new technology that completely displaces existing technology and revolutionizes the product or industry it is introduced in. It “disrupts” the regular course of functioning. For instance, computers replaced typewriters and changed the way data was stored. Harvard Business School professor Clayton M. Christensen coined the term in 1997. |
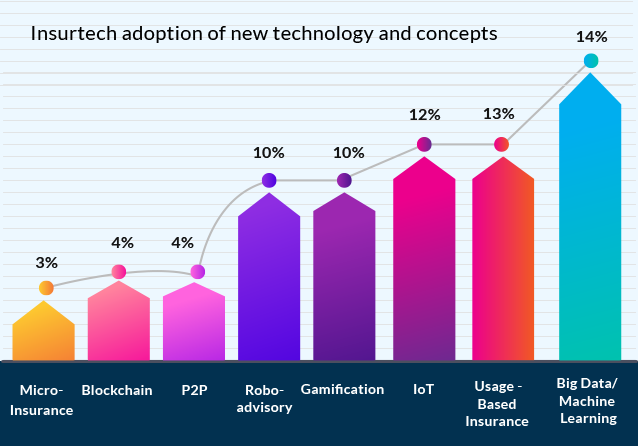
Disruptive technology examples in insurance
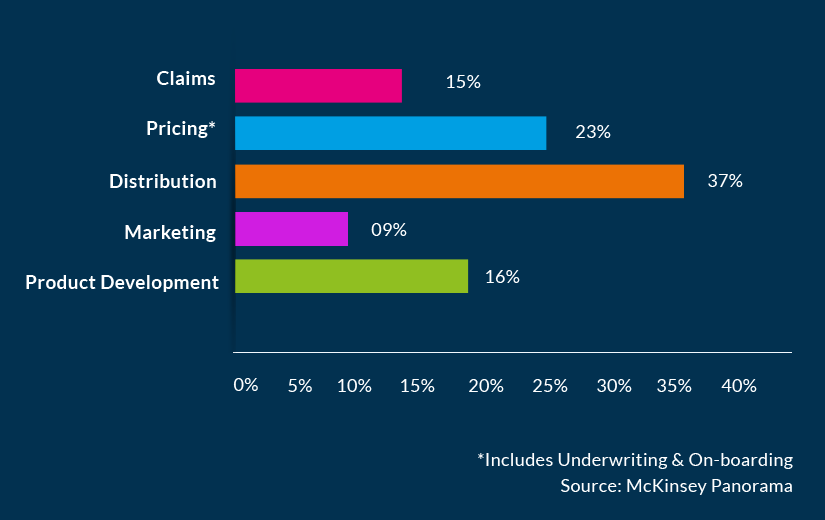
Penetration of digital innovations across the insurance value chain
Technologies to watch out for
Going by the trends in the industry, there are four technologies to watch out for that are transforming the way the insurance industry functions and are likely to disrupt the sector even further in the coming years.
1. Big data and analytics
The most important asset for insurers is data. Insurance companies have to chew through hoards of consumer and commercial information to make important decisions. For an industry that is so heavily dependent on these data points, the rise of big data technologies has been a disruptive force. For instance, predictive analytics that uses big data can accurately compute pricing and risk selection, reduce underwriting costs, improve claims triage and even catch on to emerging trends.
A Willis Towers Watson survey among U.S. property and casualty insurers found that over 90% of those surveyed felt that predictive models had a positive impact on rate accuracy, loss ratios and profitability.
In the coming years, technology tools will grow more sophisticated to maximize the efficiency, speed and accuracy of big data outcomes. Personalized policies, targeted marketing and even fraud detection will be enhanced in ways never envisioned.
2. Machine learning, artificial intelligence and robotic process automation
3. Data explosion from connected devices: IOT Technology
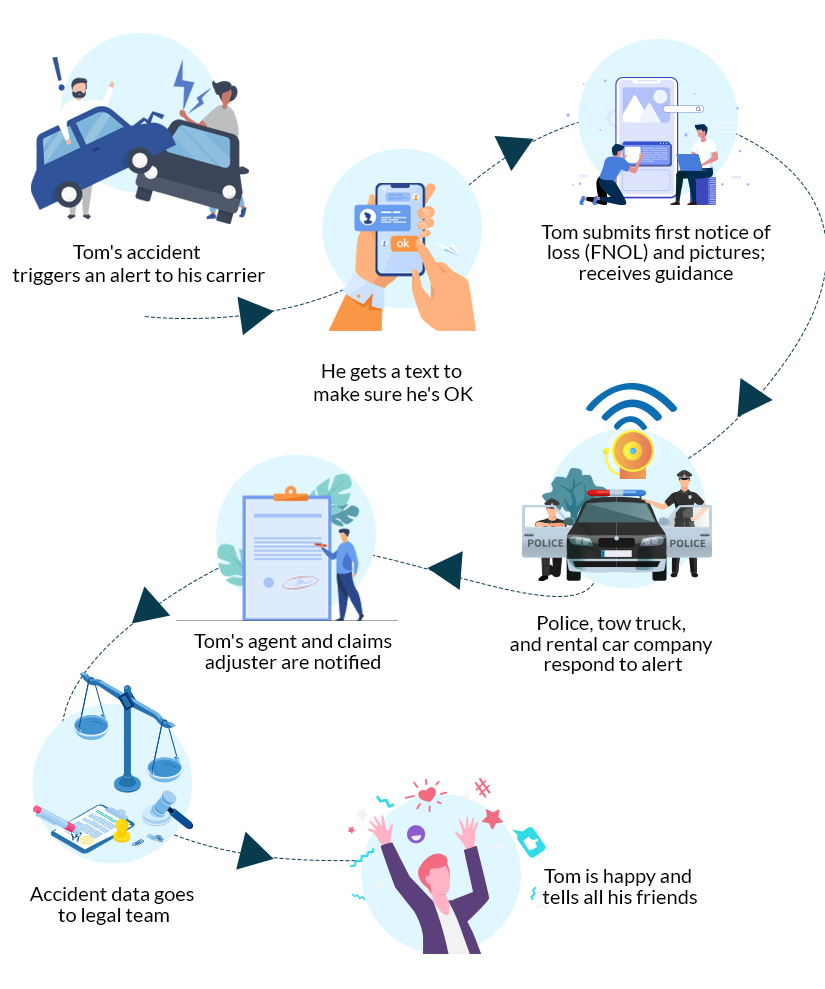
Telematics: Increasing opportunities in product innovation
IoT technology can be a game changer, completely transforming the disruptive technology meaning for insurers, especially in the personal insurance industry. Integrated technology can make data access more accurate and real-time, thereby improving the efficiency of the entire insurance process.
4. New IT architecture like blockchain
Changes to IT and data architecture can have a considerable impact on digitized insurance. For example, transitioning to cloud technology can enable efficient and cost-effective data storage.
Research indicates that 7 out of 10 insurers have adapted cloud technology for better speed, scalability and efficiency in handling insurance data.
Newer technologies like blockchain or distributed ledger technology also have immense potential in future. Some industry experts have compared the potential of blockchain technology to the internet in its ability to transform industrial practices. Blockchain in insurance can bring about greater security, fraud mitigation and efficiency for different insurance sectors. PwC estimates that blockchain technology can lead to $5-$10 billion in cost savings for reinsurers.

.png)
Comments
Post a Comment